After a long time of use, there are files that are no longer useful, and you no longer want to use those files. Additionally, these files take up a lot of space on your hard drive, so you want to delete them to free up space.
Deleting stubborn files and deleting files that cannot be deleted will help free up memory and reduce computer trash. But how to delete these stubborn files? Please read our instructions below.
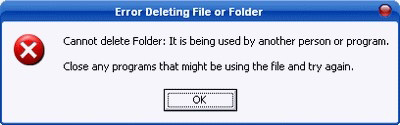
Sometimes, in some cases when you delete an unnecessary file to free up space on the hard drive, the screen displays a notification window that the file cannot be deleted:
This case often happens when the files you need to delete are contained on a hard drive partition with the file system format NTFS, and the reason why you cannot delete these files may be because the files are being used by another program. Certain programs, or files related to that file are being used, or it could also be due to an error occurring during the process of copying files to the hard drive.
If in case the file cannot be deleted because it is being used, you just need to turn off the programs that are using it and you can delete it easily. On the contrary, you cannot delete files in the usual way. Even if you don't know how, you need to reformat the hard drive to be able to erase it. However, reformatting the hard drive is one of the darkest things that computer users can think of.
1. Restart the system
Restarting the system is probably the simplest solution for the least "stubborn" files, which is to restart the system and then delete it in the usual way.
2. Use the delete command in DOS
If you apply the above method and still cannot delete the file you want to delete, you can use the delete command in DOS.
To do this, first open the DOS window by clicking the Windows Start button and selecting Run.
Next enter cmd in the Run dialog box and press Enter. At this time, the Command Prompt window will appear on the screen.
Here, you use DOS commands to go to the folder containing the file you want to delete and use the Del command in DOS to delete that file.
3. Through Task Manager
With this method, first open the Command Prompt window.
Then press the key combination Ctrl + Alt + Delete to open the Task Manager window. In the Task Manager window, select the Processes tab, and find process explorer.exe, right-click on it and select End Process.
After the process ends, your screen will completely disappear, except for the previously opened Command Prompt window. Now, you use the DEL command in DOS to delete the file you need to delete.
After executing the DEL command, enter the Explorer command into the Command Promt window so that Windows starts working again.
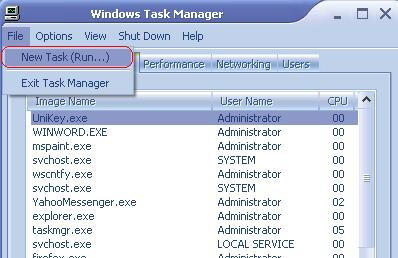
Or if, after executing the Del command, you accidentally close the Command Prompt window, press the key combination Ctrl + Alt + Delete to open the Task Manager window.
In the Task Manager window, select File > New Task (Run) and enter explorer.
However, to do this, you need to have basic knowledge of DOS as well as its commands. Therefore, if you do not have this knowledge, try applying other methods.
4. Delete the folder containing the files you want to delete
If you still cannot delete the file you want to delete, try deleting the folder containing those files. If it still doesn't work, try the following: For example, let's call the folder containing the file you need to delete A, and this folder A is in folder B. Your job is to try deleting the whole folder. B (containing folder A and the file that needs to be deleted). Sometimes they will work. However, remember that the necessary data contained in A and B must be transferred to other locations before deleting the entire folder.
5. Change File Explorer process settings
By default, File Explorer launches all its windows in a single process (explorer.exe). However, it is possible that your settings force File Explorer to launch separate processes, which may cause conflicts between other processes.
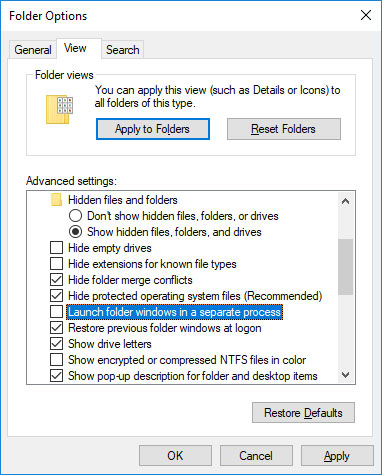
1. Press Windows + E to open File Explorer. Go to View > Options > Change folder and search options.
2. In the Folder Options window, switch to the View tab and find the Launch folder windows in a separate process option. Make sure it is unchecked. Click Apply to save any changes.
If this option is not selected initially, you can try to see if selecting it solves the problem.
6. Turn off Preview Pane in File Explorer
Previews in File Explorer can cause conflicts like the "File is open in another program" error. Press Windows + E, switch to the View tab and press Alt + P to close the Preview Pane.
After closing the Preview Pane, try the operation again and see if the "File in use" error disappears.
7. Use 3rd party applications
Sometimes, the problematic file gets locked. If trying to delete files via Command Prompt doesn't work, or if the task is too difficult, use one of these tools.
Have you ever wondered which program has a particular file or folder open? Now, you can find out. Process Explorer shows you information about processes and DLLs opened or loaded.
Process Explorer is a more powerful File Explorer. Not only does it list all running processes, but it can also tell you which process has taken your files "hostage". Just open Process Explorer Search via Find > Find Handle or DL (or press Ctrl + F), enter the file name and wait for the list of processes accessing your file.
You cannot close the process from the search window, but you can use Process Explorer or Windows Task Manager to close the application that is causing the error.
The Process Explorer screen includes two sub-windows. The top window always displays a list of currently active processes, including the name of the account that owns them, while the information displayed in the bottom window, depends on the mode in which Process Explorer is exporting. show: If it is in processing mode, you will see which processing steps the selected process in the top window opened; If Process Explorer is in DLL mode, you will see the DLL files and memory mapped files that the process has loaded. Process Explorer also has powerful search capabilities, which will quickly show you which processes have specific processes open or DLL files loaded.
Process Explorer's unique capabilities make it useful for tracking down DLL version issues or dealing with leaks, while also providing detailed information about how Windows and applications operate. .
Purple in Process Explorer is a sign that files may have been packaged. Red means the process is exiting (stopped). Green means a newly created process (just loaded). Processes in light blue are processes run by the same account that launched Process Explorer. Dark blue indicates that the process is selected (by clicking or otherwise). Pink indicates that the process is a service (like svchost.exe in the picture). If you suspend a process, it will turn dark gray until you resume (Resume).
Unlocker
If you have applied all the methods and still cannot fix the error, the last option for you is to ask for help from a 3rd party application.
One of the first applications for this was Unlocker. Unlocker is a completely free application and software. The application allows analyzing the file you need to delete to find the reason why it cannot be deleted, then, with just 1 mouse click, ends the system's connections to the file you need to delete, Finally, you can delete the file in the usual way.
Download Unlocker to your device and install it here.
Unlocker will automatically add it to the Context Menu (right-click menu). You just need to right-click on the file you want to delete, then select Unlocker.
Next click Kill Process or Unlock/Unlock All. The kill process will close the application, then you can proceed to delete the files you want to delete.
LockHunter
LockHunter will add itself to the Windows context menu. Once installed, just right-click on the locked file and select What is locking this file? This will display a window containing all the processes using the file. Now, you can choose Unlock, Delete at next system restart or Unlock & Rename file. In the example case, the author could not unlock the file, but deleting it the next time the system restarted worked.
There are also some other file deletion software that you can apply to delete this stubborn file such as: Any File Remover, IOBit Unlocker,...
Good luck!



















No comments:
Post a Comment