This freezing problem can occur haphazardly anytime. During it, either the whole system locks up or certain elements, such as the Taskbar, do not respond. You can try each of the different ways to resolve this issue and find out which one works the best for you.
Method 1: Updating the Drivers
1.Press Windows key
 + E at the same time. This opens File Explorer. Right-click on This PC, which is found on the left side of the File Explorer window. Choose Manage from the menu.
+ E at the same time. This opens File Explorer. Right-click on This PC, which is found on the left side of the File Explorer window. Choose Manage from the menu.2. In the next window that appears, choose Device Manager.
3.From the Device Manager menu, expand each category or the categories you believe need driver updates and right-click on each device. (You need to expand the Display adapters category under the graphics card to do this.) Select ‘Update Driver’ for each.
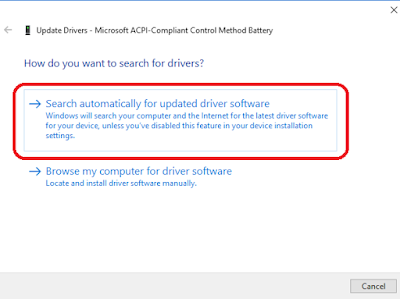
4.Finally, click Search automatically for updated driver software.
If an updated version is not found, you can also go to the device manufacturer’s website after clicking on the device’s properties and noting the current driver information. Follow the instructions on the website to search for updates there.
Method 2: Turn Off Link State Power Management
2.Find your power plan and then click Change plan settings.
3.Choose Change advanced power settings..Locate the PCI Express category and then expand it, change the setting of Link State Power Management to Off.
6.Click OK and then Apply.
Method 3: Clear your computer’s temp files
If Windows doesn’t have enough space to store temp files, it can slow down or even freeze. So you should clear them regularly.
1.Press Windows key + R , then in the Run form, type temp, %temp%, and hit Enter. This will invoke Windows Explorer with your Temp folder open, showing you all the temp files on your computer.
+ R , then in the Run form, type temp, %temp%, and hit Enter. This will invoke Windows Explorer with your Temp folder open, showing you all the temp files on your computer.
 + R , then in the Run form, type temp, %temp%, and hit Enter. This will invoke Windows Explorer with your Temp folder open, showing you all the temp files on your computer.
+ R , then in the Run form, type temp, %temp%, and hit Enter. This will invoke Windows Explorer with your Temp folder open, showing you all the temp files on your computer.
2.Select all the files in the Temp folder and delete them.
Method 4: Adjust your virtual memory
Virtual memory is basically an extension of your computer’s physical memory. It is a combination of RAM and a portion of your hard drive. If your computer runs out of RAM when performing an intensive task, Windows will dip into virtual memory for temporary file storage.
2.Go to the Advanced tab>Settings>Advanced tab again>Change… in the Virtual memory section.
3.Ensure the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives checkbox is NOT ticked.
4.select your windows drive (the hard drive or partition that has Windows installed on it – usually C:), and enter an Initial size and Maximum size for your virtual memory:
- Initial size – This value varies, depending on your computer. If you’re not sure what value to use, just enter whatever the number is in the Recommended category.
- Maximum size – Don’t set this value too high. It should be about 1.5 times the size of your physical RAM. e.g. A PC with 4 GB (4096 MB) of RAM should have no more than about 6,144 MB virtual memory (4096 MB x 1.5).
Once you’ve entered your virtual memory values, click Set, then click OK to continue.
Method 5: Run a memory check
A faulty memory card is one of the most common causes of computer freezes. So before you invest in a new computer, check to see if your memory card is at fault. Microsoft has a built-in tool to help you do this.
2.If you want to check for problems immediately, click Restart now and check for problems(recommended). If you want to check later, click Check for problems the next time I start my computer.
3.Windows will then restart, and you’ll see this page showing the progress of the check and the number of passes it will run on memory.
Method 6: Run Disk Check
If you’ve come this far, it’s time for you to check if your hard disk is at fault. Don’t worry, this is easy to do, because Windows has a built in tool for the job…
1.Close all open programs and files.
2.Click Start > File Explorer > This PC.
3.Locate the hard drive you’d like to check, right-click on it and choose Properties.
4.Go to the Tools tab and click Check.
5.If your hard disk drive is problem-free, you’ll see this:
This suggests your hard disk is NOT the problem, and you can move on to the next fix below.
Method 7: Run System File Checker
Corrupt or missed system files can cause Windows to randomly freeze. But don’t worry, Microsoft makes it easy for you to get your original system files back. It has an in-built tool called System File Checker that will restore any broken or missing system files that could be causing your PC to freeze. Here’s how to use it:
1.Press the Windows key and then type cmd (DON’T press Enter). Windows will display a list of programs that match your search. Right-click Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
and then type cmd (DON’T press Enter). Windows will display a list of programs that match your search. Right-click Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
 and then type cmd (DON’T press Enter). Windows will display a list of programs that match your search. Right-click Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
and then type cmd (DON’T press Enter). Windows will display a list of programs that match your search. Right-click Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
If prompted to provide administrator permission, click Yes.
2.In the black Command Prompt window, type:
sfc /scannow
Then press Enter on your keyboard.
Windows will scan your system for corrupted files, and attempt to fix any it finds. The results will display in this window, so please leave it open until the operation is complete.
Video:
Video:































No comments:
Post a Comment